Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kawaguchi, Munemichi; Miyahara, Shinya; Uno, Masayoshi*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 56(6), p.513 - 520, 2019/06
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:21.22(Nuclear Science & Technology)This study revealed melting points and thermal conductivities of four samples generated by sodium-concrete reaction (SCR). We prepared the samples using two methods such as firing mixtures of sodium and grinded concrete powder, and sampling depositions after the SCR experiments. In the former, the mixing ratios were determined from the past experiment. The latter simulated the more realistic conditions such as the temperature history and the distribution of Na and concrete. The thermogravimetry-differential thermal analyzer (TG-DTA) measurement showed the melting points were 865-942 C, but those of the samples containing metallic Na couldn't be clarified. In the two more realistic samples, the compression moldings in a furnace were observed. The observation revealed the softening temperature was 800-840
C, but those of the samples containing metallic Na couldn't be clarified. In the two more realistic samples, the compression moldings in a furnace were observed. The observation revealed the softening temperature was 800-840 C and the melting point was 840-850
C and the melting point was 840-850 C, which was 10-20
C, which was 10-20 C lower than the TG-DTA results. The thermodynamics calculation of FactSage 7.2 revealed the temperature of the onset of melting was caused by melting of the some components such as Na
C lower than the TG-DTA results. The thermodynamics calculation of FactSage 7.2 revealed the temperature of the onset of melting was caused by melting of the some components such as Na SiO
SiO and/or Na
and/or Na SiO
SiO . Moreover, the thermal conductivity was
. Moreover, the thermal conductivity was  =1-3W/m-K, which was comparable to xNa
=1-3W/m-K, which was comparable to xNa O-1-xSiO
O-1-xSiO (x=0.5, 0.33, 0.25), and those at 700
(x=0.5, 0.33, 0.25), and those at 700 C were explained by the equation of
C were explained by the equation of 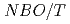 .
.
Kitamura, Akira; Ito, Miki*; Akagi, Yosuke*; Yoshida, Yasushi*
no journal, ,
Effect of carbonate concentration and redox conditions on uranium solubility under geological disposal conditions was investigated. The applicability of predicted values using thermodynamic database was verified.
Kawaguchi, Munemichi*; Miyahara, Shinya; Uno, Masayoshi*
no journal, ,
Though the steel liner is set up to prevent Na contacting with the concrete in the case of Na leakage in the Na-cooled fast reactor, it is important to grasp the Na-concrete reaction mechanism. The past studies have focused on the thermal, concrete ablation and hydrogen release behaviors. Also the natural termination of this reaction was confirmed experimentally; it was pointed out that the sedimentation of the reaction products was one of the terminating causes. This paper is reported on a discussion such as thermodynamics calculations of the reaction products, related with the Na-concrete reaction terminating study.
Yamamoto, Ikuo*; Uno, Masayoshi*; Miyahara, Shinya; Kawaguchi, Munemichi
no journal, ,
An estimation technology and reaction model on phase equilibrium state of fuel debris under sodium using thermodynamics calculation has been developed. In this study, the reaction products were calculated in sodium uranate system by thermodynamics calculation using Thermo-Calc.